BIOFUEL - THE FUEL OF THE FUTURE
How to Make
Biofuels
Biofuel is considered to be the most pure and the easiest
available fuels on the planet. Also known as agrofuel, they
are classified into gas, liquid and solid form derived from
biomass. Most of the people would be very happy to know that
most of the forms of biofuels can be easily manufactured.
One of the key features of biofuels is that they are better
than other forms of fuels like petrol or diesel that is
manufactured by most of the big oil manufacturing companies.
Most of the diesel engines would work more efficiently and
even last longer with the use of these home made biofuels.
These fuels are also very clean and environment friendly and
also encourage the recycling process as most of them are
manufactured from waste products.
There are various forms of biofuels and most of them are
made through a detailed process having various stages. Most
of the animal fats, vegetables and oils contain glycerin and
are thus called triglycerides. In the process of
manufacturing the biofuels, all the fats and oils are turned
into esters, separating the glycerin. At the end of the
process, all the glycerin sinks down at the bottom and all
the biofuel rests at the top. The process through which the
glycerin is separated from the biodiesel is known as
transesterification. This process also uses lye as a
catalyst in the whole process. Some of the chemicals which
are used in the manufacturing of biofuels are ethanol or
methanol which brings into use methyl esters. Methanol is
derived from fossil fuels while ethanol is derived from
plants. One of the advantages of using ethanol is that they
can be distilled even at the home without any problem.
The process of manufacturing biofuel can be classified in
the following stages. These stages are:
Filtering: In this process, waste vegetable oil is filtered
to remove all the food particles. This process generally
involves warming up the liquid a little. After warming up
the liquid, it can be filtered with the use of coffee
filter.
Removing of water: All the water contained in the residual
gangue has to be removed which will make the reaction
faster. The water can be easily removed by making the liquid
boil at 100 degree C for sometime.
Titration: This process is carried out to determine the
amount of lye that would be required. This process is the
most crucial and the most important stage of biofuel
manufacturing.
Preparation of sodium methoxide: In this process, methanol
is mixed with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium methoxide.
In most of the cases, the quantity of methanol used is
generally 20 percent of waste vegetable oil.
Heating and mixing: The residue is heated in between 50 to
60 degree C after which it is mixed well. It should be
remembered that process should be done carefully avoiding
splashing of the liquid.
Settling and separation: After mixing the liquid, it has to
be allowed to cool down. After the cooling process, the
biofuel will be found floating at the top while the heavier
glycerin would be found at the bottom. The glycerin can be
easily separated by allowing it to drain out from the
bottom. The person is left over with pure biofuel which can
be used for various purposes.
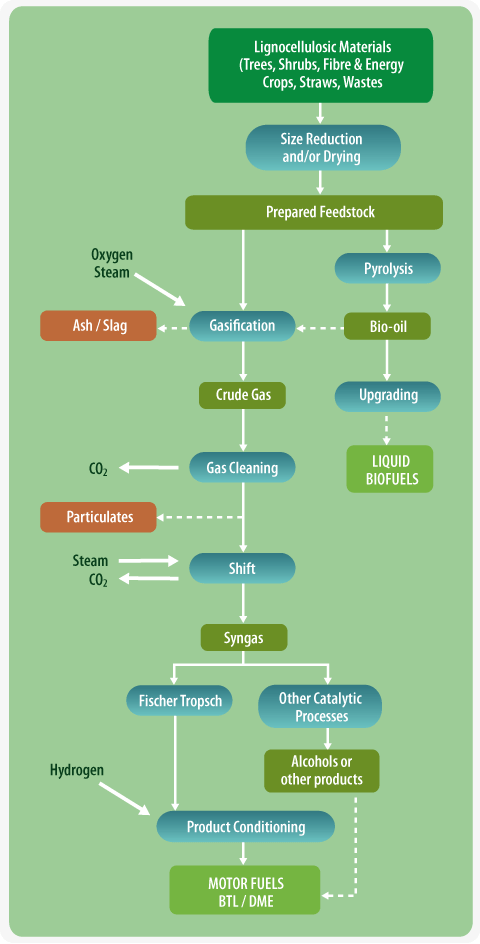
Biochemical Routes to Liquid Biofuels

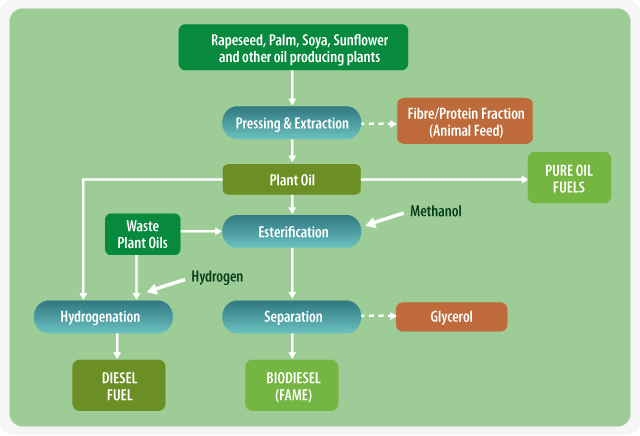
Production of Biofuels From Vegetable Oils
Thermochemical Routes to Liquid Biofuels